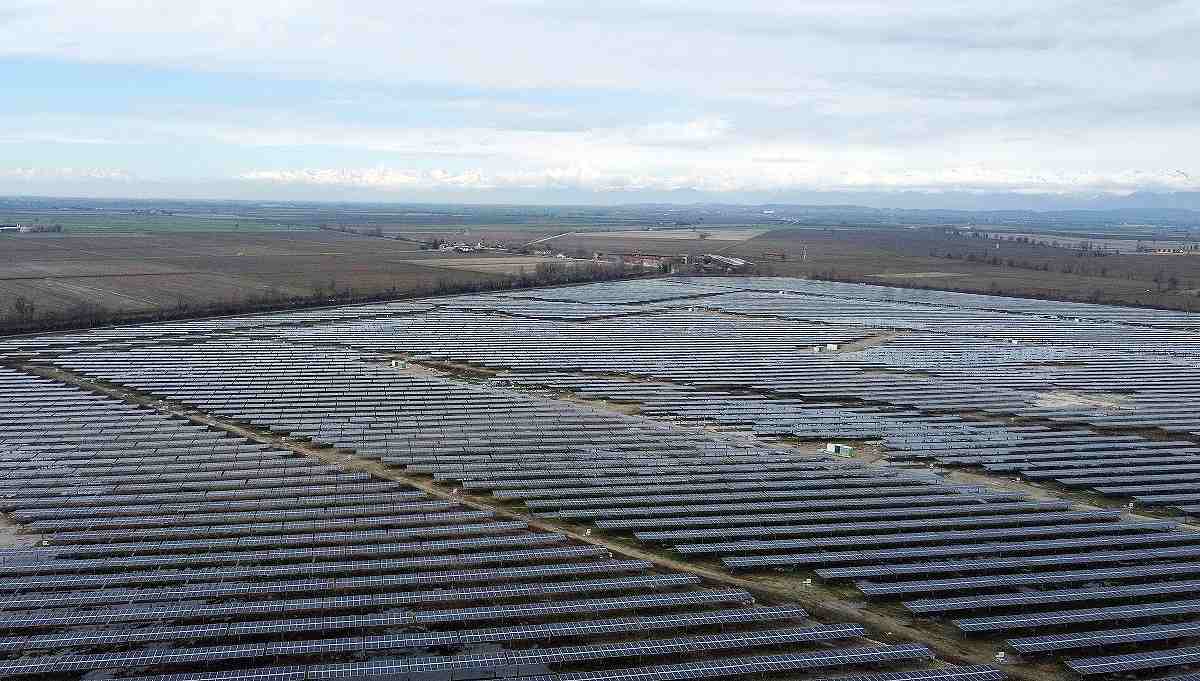
540 W bifacial solar panels are seen at a solar panels park by energy supplier Enel Green Power, in Turin on March 5.
12:49 JST, May 23, 2024
ROME (Reuters) — Italy’s rightwing coalition on May 6 passed rules curbing the installation of solar panels on agricultural land, ministers said, in a move that triggered criticism as it could undermine Rome’s decarbonization goals.
The new rules, part of a broader package of measures to protect farming and fisheries, included a ban on the installation of photovoltaic systems with modules placed on the ground in areas classified as agricultural.
“We put an end to the wild installation of ground-mounted photovoltaic [panels],” Agriculture Minister Francesco Lollobrigida told a news conference after the cabinet meeting that approved the measures.
Agricultural lobbies — key supporters of Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni’s right-wing government — had long called for limitations to the panels, saying they were incompatible with cultivation.
In contrast, environmental associations accused the government of undermining green goals, agreeing with partners from the Group of Seven wealthy nations.
At the end of a meeting of G7 energy ministers, Italy committed to triple installed renewable energy capacity by 2030 and phase out coal-fired power plants in the first half of the next decade.
Energy Minister Gilberto Pichetto Fratin — who government officials said had initially opposed the plan — told reporters the new curbs would not jeopardize a government goal to install around 38 gigawatts (GW) by 2030 through photovoltaic plants.
Lollobrigida said the scheme does not target agri-voltaic projects, which place solar panels over fields and vineyards to get double use out of the land by producing power during periods of heavy sunlight, while still allowing crops to grow.
The government’s package is now subject to scrutiny by both houses of Parliament, which are allowed to amend it.
Limits on solar plants could negatively impact energy companies including ERG and ALERION, which have growth targets in the solar sector, financial analysts at Italian broker Equita said.
On the other hand, a slowdown in the development of solar capacity could be positive for power generators including Enel, A2A and IREN, which may suffer pressure on prices if solar energy accelerates, the analysts said.
Italy last year added nearly 6 GW in renewable energy capacity, mainly through the development of small solar plants, with wind projects accounting for only 8% of the new green capacity.
Top Articles in Science & Nature
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Japan to Face Shortfall of 3.39 Million Workers in AI, Robotics in 2040; Clerical Workers Seen to Be in Surplus
-

Record 700 Startups to Gather at SusHi Tech Tokyo in April; Event Will Center on Themes Like Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
-

iPS Treatments Pass Key Milestone, but Broader Applications Far from Guaranteed
-

iPS Cell Products for Parkinson’s, Heart Disease OK’d for Commercialization by Japan Health Ministry Panel
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Japan PM Takaichi’s Cabinet Resigns en Masse
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Israeli Ambassador to Japan Speaks about Japan’s Role in the Reconstruction of Gaza
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Videos Plagiarized, Reposted with False Subtitles Claiming ‘Ryukyu Belongs to China’; Anti-China False Information Also Posted in Japan