3 Japanese Carmakers Eye Joint Software Development; Toyota, Honda, Nissan See Benefits in Standardization

The Economy, Trade and Industry Ministry building in Chiyoda Ward, Tokyo.
14:31 JST, May 16, 2024
Toyota Motor Corp., Honda Motor Co. and Nissan Motor Co. are considering a plan to work together on the development of in-car software, The Yomiuri Shimbun has learned.
The three major Japanese automakers are pushing ahead with a shift away from independently developing this technology and expect that standardizing some parts could lead to greater development efficiency.
At a time when U.S. and Chinese automakers are striding ahead in digitization technologies for electric vehicles, the three Japanese vehicle manufacturers aim to adopt a cooperative approach to combat the challenges posed by their rivals.
The Economy, Trade and Industry Ministry and the Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism Ministry will reflect the plan in a digital strategy for automobiles that will be compiled this month. Specific measures will be discussed from summer and beyond, with the automakers aiming to begin their software partnership from fiscal 2025 or later. The initiative could be expanded to other domestic automakers including Suzuki Motor Corp., Mazda Motor Corp., Subaru Corp. and Mitsubishi Motors Corp.
Software controls many basic functions of modern vehicles, including the steering and brakes. Software plays a pivotal role in vehicle performance, so superiority in this field directly affects the competitiveness of each automaker.
The three automakers are expected to consider standardizing the basic platform for an application programming interface (API), which serves as the link between the software and other systems. The three automakers believe that doing so would enable them to overcome obstacles in enabling the installation of parts such as batteries and sensors. There also are expectations that this will lower barriers to entering the industry and encourage the development of various services by external companies, similar to the way smartphones apps have evolved. Alignment also will become easier between services such as voice recognition, maps and autonomous driving.
However, discussions on issues including fairness among the automakers when it comes to the selection of new specifications will be unavoidable. While each automaker might agree on the overall necessity of this approach, the details of the process of turning it into reality will present many hurdles.
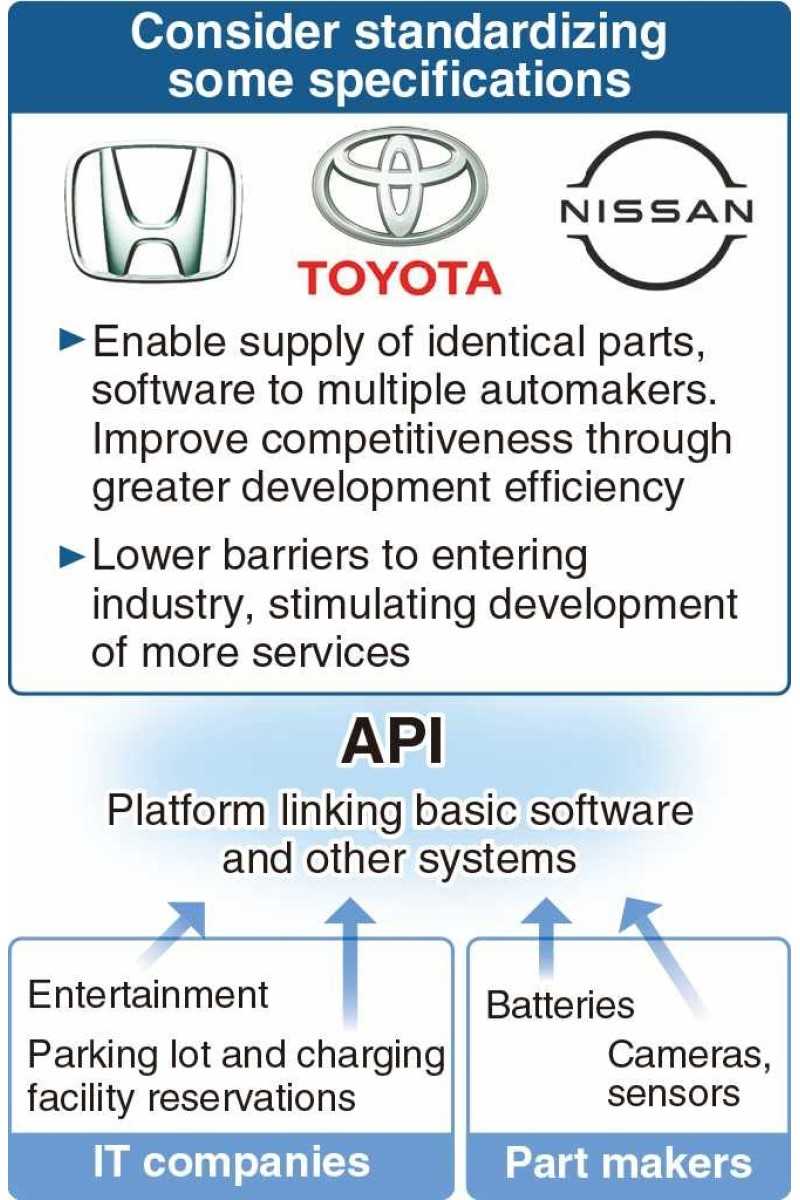
How automakers might cooperate on software development
Despite this, there is an urgent need to initiate cooperation in light of vehicle design and development concepts being revamped around the world. Newly emerging automakers in the United States and China are pursuing strategies to boost vehicle value by focusing on software design and development.
U.S. automaker Tesla Inc. updates its vehicle software through the internet, just as is done with smartphones. This allows vehicle features to be enhanced. Additional features can be obtained for a fee, so Tesla has successfully created a way to generate money from vehicles after they have been sold. China has pushed ahead with efforts to standardize an API for the industry since 2021, and it has started equipping vehicles with cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence.
Nurturing human resources capable of developing this software will be a key task for the Japanese automakers. They will identify areas in which cooperation across company lines will be possible and create an environment conducive to allocating employees to cutting-edge fields such as autonomous driving.
Top Articles in Business
-

Prudential Life Insurance Plans to Fully Compensate for Damages Caused by Fraudulent Actions Without Waiting for Third-Party Committee Review
-

Japan, U.S. Name 3 Inaugural Investment Projects; Reached Agreement After Considerable Difficulty
-

Japan’s Major Real Estate Firms Expanding Overseas Businesses to Secure Future Growth, Focusing on Europe, U.S., Asia
-

SoftBank Launches AI Service for Call Centers That Converts Harsh Customer Voices into Softer Voices
-

Transport Companies See Opportunity in Narita Expansion; Airlines, Railways Prepare to Meet Expected Growth in Demand
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Producer Behind Pop Group XG Arrested for Cocaine Possession
-

Japan PM Takaichi’s Cabinet Resigns en Masse
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Israeli Ambassador to Japan Speaks about Japan’s Role in the Reconstruction of Gaza
-

Videos Plagiarized, Reposted with False Subtitles Claiming ‘Ryukyu Belongs to China’; Anti-China False Information Also Posted in Japan

























