Famous Red Gate at Univ. of Tokyo Said in Danger of Collapse in Case of Earthquake or Strong Wind; Reinforcement Work Planned
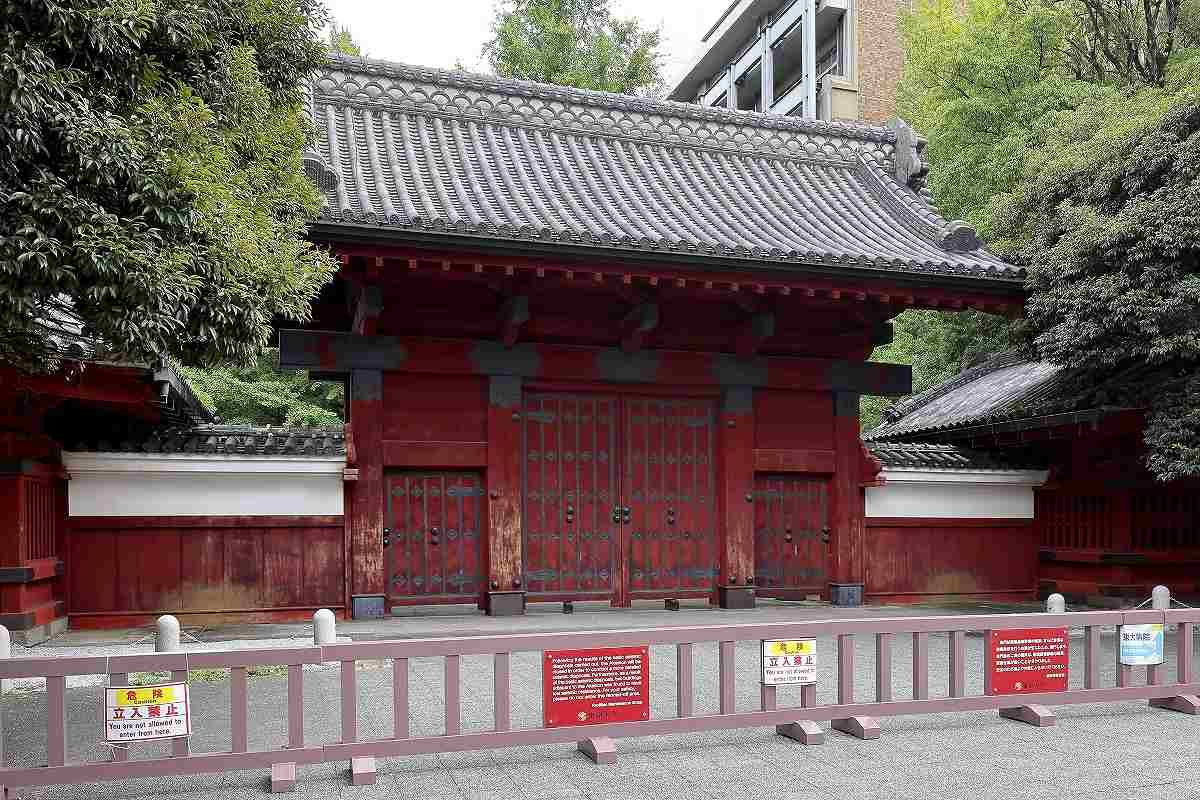

The famous Akamon Gate of the University of Tokyo in Bunkyo Ward has been closed since 2021.
12:40 JST, October 11, 2024
Generations of the nation’s top scholars and leaders have passed through it on their way to building an advanced society. Now the Akamon Gate, the distinctive red gate on the University of Tokyo’s campus in central Tokyo, itself is in danger of collapse.
Seismic experts have deemed that the gate, which dates back nearly 200 years, has weakened to the point where it could collapse in a major earthquake or typhoon-strength winds.
The gate on the Hongo campus in Bunkyo Ward has been closed since February 2021 as a structural inspection is carried out. The university is looking into starting reinforcement work from the next fiscal year at the earliest, with the hope of opening it back up as soon as possible.
The Akamon Gate, officially known as a “goshudenmon,” is the oldest remaining structure on the campus and has been designatedas an important cultural property. It was constructed in 1827 by Nariyasu Maeda, the lord of the Kaga domain, to welcome his new bride, a daughter of the 11th shogun of the Tokugawa Shougnate.
Originally part of the Edo residence of Maeda clan, it remained intact when the site became part of the University of Tokyo during the Meiji era (1868-1912). It also survived the Kanto Great Earthquake and the Tokyo air raids during World War II.
In 2018, the Cultural Affairs Agency requested that owners or administrators of important cultural properties implement reinforcement. In response, the university commissioned an expert to conduct a visual check of the structure.
The expert found possible deterioration at the base of the columns and in the roof joints, leading to the closure of the gate as a precaution.
The gate escaped demolition when a more detailed inspection by university researchers revealed there was no extensive damage at the bases of the columns and the joints were tight enough.
Even so, it was determined that a strong force from an earthquake or powerful wind exerted on the gate could cause it to collapse outward from the campus, endangering pedestrians on the sidewalk.
One factor is that the construction method for the tiled roof made it extremely heavy. It weighs about 200 to 220 kilograms per square meter, accounting for 80% of the estimated 40 tons of the entire gate. The inspection also found that the center of the gravity sits slightly on the street side of the gate.
The university plans to improve the gate’s earthquake resistance by reinforcing the column bases and making the roof lighter by reducing the amount of dirt used to attach the tiles.
As it is important to first come up with a method that does not impair the esthetic value of the gate, there is no timetable for the restoration and reopening.
“It is painful that the gate remains closed, but we want to proceed with repairs carefully so that it can be preserved for generations to come,” said Prof. Kaori Fujita, who was involved in the inspection.
Top Articles in Society
-

JAL, ANA Cancel Flights During 3-day Holiday Weekend due to Blizzard
-

Record-Breaking Snow Cripples Public Transport in Hokkaido; 7,000 People Stay Overnight at New Chitose Airport
-

Australian Woman Dies After Mishap on Ski Lift in Nagano Prefecture
-

Foreign Snowboarder in Serious Condition After Hanging in Midair from Chairlift in Nagano Prefecture
-

Train Services in Tokyo Resume Following Power Outage That Suspended Yamanote, Keihin-Tohoku Lines (Update 4)
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Univ. in Japan, Tokyo-Based Startup to Develop Satellite for Disaster Prevention Measures, Bears
-

JAL, ANA Cancel Flights During 3-day Holiday Weekend due to Blizzard
-

China Confirmed to Be Operating Drilling Vessel Near Japan-China Median Line
-

China Eyes Rare Earth Foothold in Malaysia to Maintain Dominance, Counter Japan, U.S.
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time