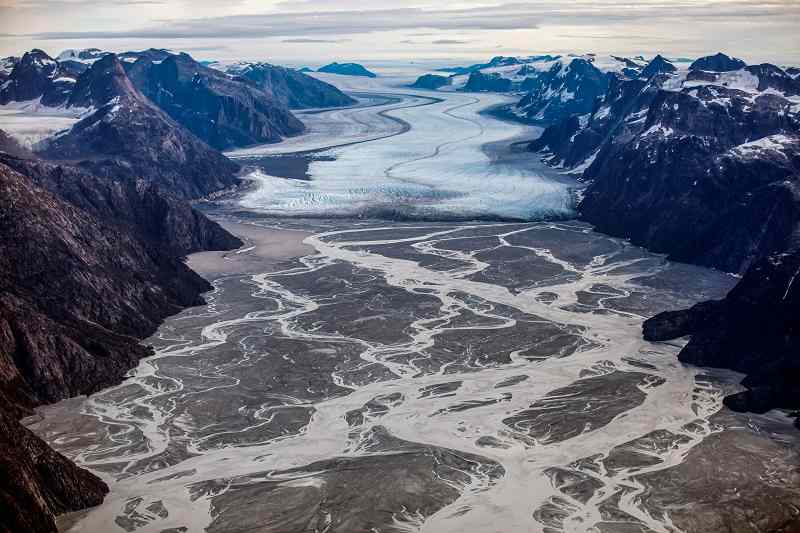

The melting Sermeq glacier, located around 80 km south of Nuuk, is photographed in this aerial over Greenland, September 11, 2021.
10:34 JST, September 1, 2021
An artist illustration : The highest point where rainfall has been observed
Research institutes in Japan and other countries have reported one after another on climate change in Greenland, which is mostly located in the Arctic Circle.
It has become apparent that rainfall has increased on the ice sheet covering most of the island in recent years, including at the highest point of 3,216 meters above sea level, where rainfall — not snowfall — has been observed for the first time. Those cases are believed to have occurred from the effect of global warming that is fast spreading in the Arctic Circle.
The Meteorological Agency’s Meteorological Research Institute on Monday released the result of its analysis of the amount of rainfalls on the ice sheet from 1980 to 2019. After correcting the random variation of the data, it has become clear that the annual rainfall increased by 14 billion tons, or 1.7 times, in 40 years. The proportion of rainfall among all precipitation rose by 1.2 percentage points to 3.6% during that time.
Since 2000, heavy September rainfalls of 50 millimeters or more per hour have been observed six times, even though it had hardly ever been observed in the past. When rain falls heavily in a short period of time, rainwater streams through cracks in the ice and seeps into the ground below, which makes the ice sheet susceptible to displacement and contributes to ablation.
The rainfall on the summit of the ice sheet was reported by the National Snow and Ice Data Center of the United States, which said an observatory at the summit recorded rainfall from Aug. 14 to 16. Apparently, it was the first rainfall observed there since observations started in 1989.
A report published this month by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change of the United Nations noted that continued ice loss over the 21st century is virtually certain for the ice sheet in Greenland.
“It’s become apparent that rainfall is increasing along with the melting of the ice sheet. I didn’t expect there would be a rainfall on the highest point on the ice sheet in the next few years. I am shocked by the rapid environmental change,” said Masashi Niwano, a senior researcher of the Meteorological Research Institute.
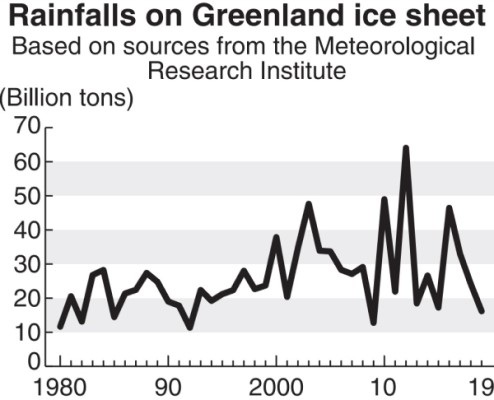
An artist illustration : Rainfalls on Greenland ice sheet.
Based on sources from the Meteorological Research Institute
Top Articles in Science & Nature
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Japan to Face Shortfall of 3.39 Million Workers in AI, Robotics in 2040; Clerical Workers Seen to Be in Surplus
-

Record 700 Startups to Gather at SusHi Tech Tokyo in April; Event Will Center on Themes Like Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
-

iPS Treatments Pass Key Milestone, but Broader Applications Far from Guaranteed
-

iPS Cell Products for Parkinson’s, Heart Disease OK’d for Commercialization by Japan Health Ministry Panel
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Japan PM Takaichi’s Cabinet Resigns en Masse
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Israeli Ambassador to Japan Speaks about Japan’s Role in the Reconstruction of Gaza
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Videos Plagiarized, Reposted with False Subtitles Claiming ‘Ryukyu Belongs to China’; Anti-China False Information Also Posted in Japan























