Retrieval of Fuel Debris from Fukushima Reactor Suspended Again; TEPCO Unable to Predict When Work Might Resume

Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings Inc. headquarters in Chiyoda Ward, Tokyo
15:50 JST, September 18, 2024
Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. has once more suspended its trial retrieval of nuclear fuel debris from the No. 2 reactor at the Fukushima No. 1 nuclear power plant, this time due to the failure of cameras attached to the retrieval device.
Because the cameras were not working properly, the situation inside the primary containment vessel could not be checked. TEPCO said it will investigate the cause of the failure, but it could not predict when the work will resume.
The trial retrieval of nuclear fuel debris was initially scheduled to begin Aug. 22. However, a procedural error was discovered during the preparatory process and the plan was halted. Efforts resumed about three weeks later on Sept. 10.
This was the first trial for the retrieval of debris to have started after the nuclear accident in March 2011, in the wake of the Great East Japan Earthquake and subsequent tsunami.
The radiation levels inside the containment vessel are extremely high, making it easy for devices to fail or malfunction. The plan was to push a device resembling a fishing rod, which extends up to 22 meters, into the side of the vessel, and attempt to retrieve up to 3 grams of debris with a claw attached to the end. The device was previously used to take photographs inside the No. 2 reactor, and it was adapted for this operation.
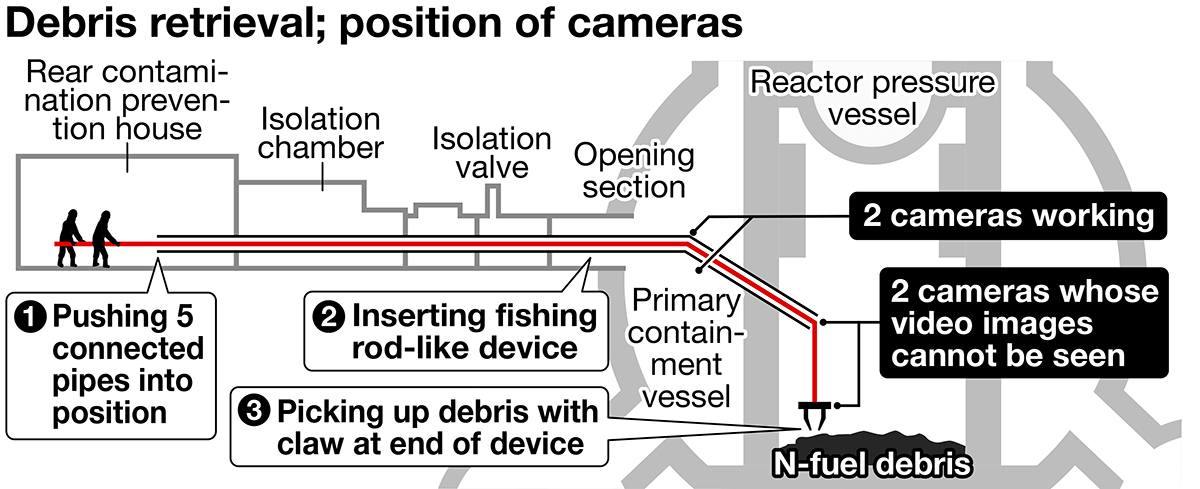
According to TEPCO, four cameras were attached to the device and the retrieval operation was to be carried out remotely while observing the video feeds. On Tuesday, a check of the device started at around 6 a.m., but the video from two cameras on the tip of the device was not being properly displayed, and the operation could not continue.
The device’s end claw made contact with debris at the bottom of the reactor containment vessel on Saturday. When the device was inspected the following day, video images could be seen.
Nuclear fuel from Reactor Nos. 1 to 3 melted and fell down during the 2011 nuclear accident, mixing with the structures inside the reactors and solidifying, generating an estimated 880 tons of debris.
Retrieval of the debris is considered to be the most difficult part of the decommissioning, which the government and TEPCO are aiming to complete by 2051.
Top Articles in Society
-

Producer Behind Pop Group XG Arrested for Cocaine Possession
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Man Infected with Measles May Have Come in Contact with Many People in Tokyo, Went to Store, Restaurant Around When Symptoms Emerged
-

Woman with Measles Visited Hospital in Tokyo Multiple Times Before Being Diagnosed with Disease
-

Australian Woman Dies After Mishap on Ski Lift in Nagano Prefecture
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Producer Behind Pop Group XG Arrested for Cocaine Possession
-

Japan PM Takaichi’s Cabinet Resigns en Masse
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Israeli Ambassador to Japan Speaks about Japan’s Role in the Reconstruction of Gaza
-

Videos Plagiarized, Reposted with False Subtitles Claiming ‘Ryukyu Belongs to China’; Anti-China False Information Also Posted in Japan