12:22 JST, June 15, 2023
Sperm whales and other cetaceans that come to the waters around Hokkaido in autumn having differing preferences when it comes to things like ocean depth and temperature, according to a team of researchers from Kyoto University and Hokkaido University.
The team analyzed the distribution of cetaceans in Hokkaido’s coastal areas and the relationship with the marine environment. Drawn from more than 10 years of observation, the results will likely contribute to the conservation of cetaceans.
The analysis has recently been published in an international academic journal.
A variety of cetaceans migrate to the waters around Hokkaido each autumn, but details about their ecology are unknown.
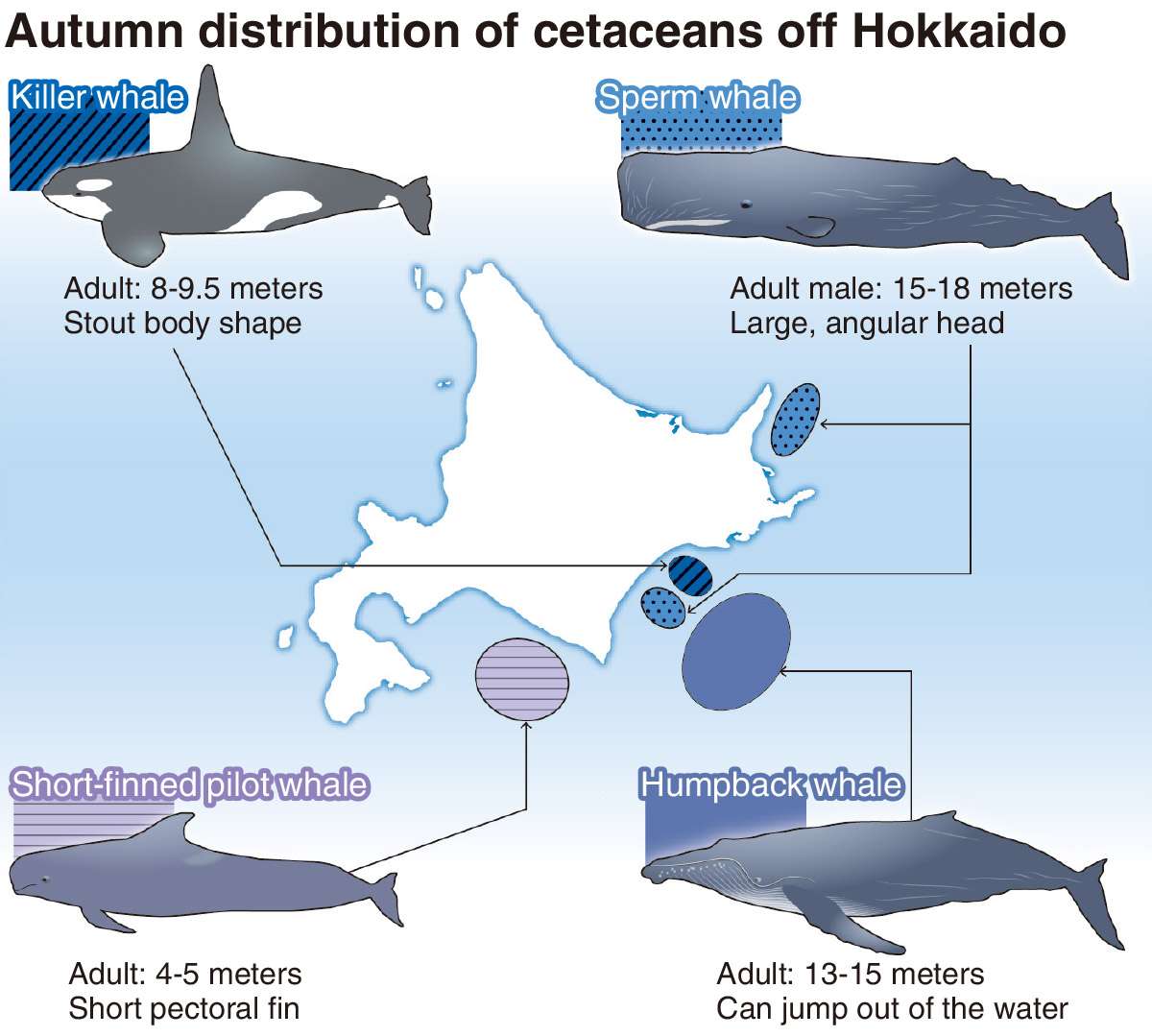
The team conducted surveys on 21 occasions in September and October from 2009 to 2021 aboard a Hokkaido University training ship. Members studied 11 species, including sperm whales, based on such factors as where they were found, water depth, seafloor topography and seawater temperature, and analyzed the relationship between the distribution of these species and the marine environment.
Sperm whales were found mainly on the southern coast of the Shiretoko Peninsula, where the seafloor slopes steeply. They are believed to prefer this area because sperm whales dive into steep underwater valleys at depths of more than 3,000 meters to hunt for food. These marine areas are said to be abundant feeding grounds for them.
The water temperature is relatively high on the west side of Cape Erimo, which juts out to the south, and many short-finned pilot whales that prefer warmer water were found there.
Killer whales, on the other hand, were found on the eastern side of the cape and also around Shiretoko Peninsula, where the water temperature is lower.
“It’s important to continue the research, so as to gauge the recovery in the cetacean population following the cessation of whaling as well as the effects of rising ocean temperatures due to global warming,” said Yoko Mitani, a member of the team and a researcher at the Wildlife Research Center of Kyoto University.
Hiroto Murase, associate professor of cetacean biology at Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology, said: “Cetaceans generally have a long life span, so changes in the population and distribution tend to occur slowly. I hope that with further research, more information will be compiled.”
Top Articles in Science & Nature
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Japan to Face Shortfall of 3.39 Million Workers in AI, Robotics in 2040; Clerical Workers Seen to Be in Surplus
-

Record 700 Startups to Gather at SusHi Tech Tokyo in April; Event Will Center on Themes Like Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
-

iPS Treatments Pass Key Milestone, but Broader Applications Far from Guaranteed
-

iPS Cell Products for Parkinson’s, Heart Disease OK’d for Commercialization by Japan Health Ministry Panel
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Japan PM Takaichi’s Cabinet Resigns en Masse
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Israeli Ambassador to Japan Speaks about Japan’s Role in the Reconstruction of Gaza
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Videos Plagiarized, Reposted with False Subtitles Claiming ‘Ryukyu Belongs to China’; Anti-China False Information Also Posted in Japan






















