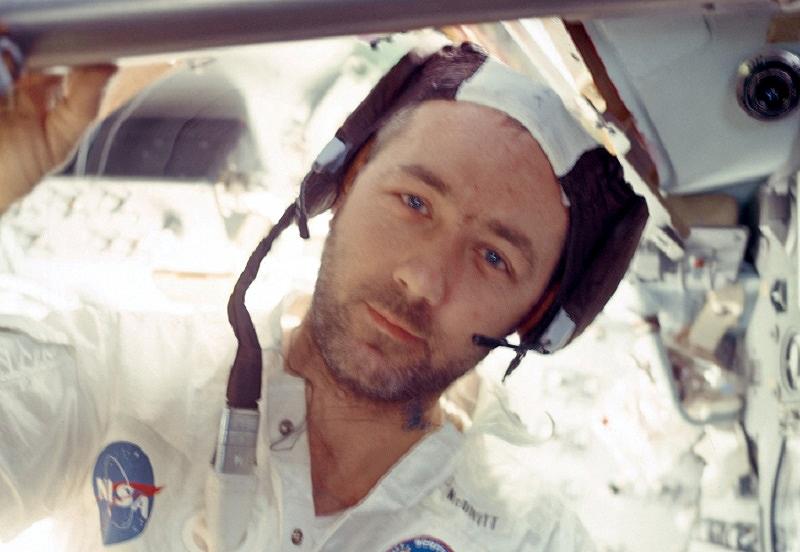
James McDivitt is seen on board the Lunar Module during the Apollo 9 mission on March 6, 1969.
16:29 JST, October 28, 2022
WASHINGTON (Reuters) — James McDivitt, a former U.S. astronaut who commanded some of NASA’s earliest and most ambitious missions in space, died in his sleep at age 93, NASA said in a statement on Oct. 17.
McDivitt, who was selected for NASA’s second astronaut class in 1962, was the commanding pilot for the U.S. space agency’s Gemini 4 mission in 1965 and Apollo 9 in 1969, a mission that helped pave the way for the first human lunar landing.
The astronaut and retired U.S. Air Force test pilot died “peacefully in his sleep surrounded by his family and friends in Tucson, Arizona,” NASA said in a statement.
McDivitt’s two missions were instrumental in the Cold War-driven space race between the United States and Soviet Union, whose string of early spaceflight successes galvanized Washington to pursue rival achievements such as the Apollo 11 first crewed moon-landing in July of 1969.
The fourth mission under Project Gemini, a precursor to NASA’s Apollo program, marked McDivitt’s first flight to space.
During that four-day spaceflight, he oversaw the first American spacewalk in which fellow astronaut Ed White floated outside of their spacecraft for the first time, tethered by a cord.
McDivitt later joined two astronauts as commander of the Apollo 9 mission, a crucial debut flight test of NASA’s Lunar Module that would later land astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin on the moon during the Apollo 11 mission.
Top Articles in Science & Nature
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Japan to Face Shortfall of 3.39 Million Workers in AI, Robotics in 2040; Clerical Workers Seen to Be in Surplus
-

Record 700 Startups to Gather at SusHi Tech Tokyo in April; Event Will Center on Themes Like Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
-

iPS Treatments Pass Key Milestone, but Broader Applications Far from Guaranteed
-

iPS Cell Products for Parkinson’s, Heart Disease OK’d for Commercialization by Japan Health Ministry Panel
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Japan PM Takaichi’s Cabinet Resigns en Masse
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Israeli Ambassador to Japan Speaks about Japan’s Role in the Reconstruction of Gaza
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Videos Plagiarized, Reposted with False Subtitles Claiming ‘Ryukyu Belongs to China’; Anti-China False Information Also Posted in Japan