China Strikes Friendly Pose Ahead of Upper House Poll,But Provocative Actions at Sea Undermine Message
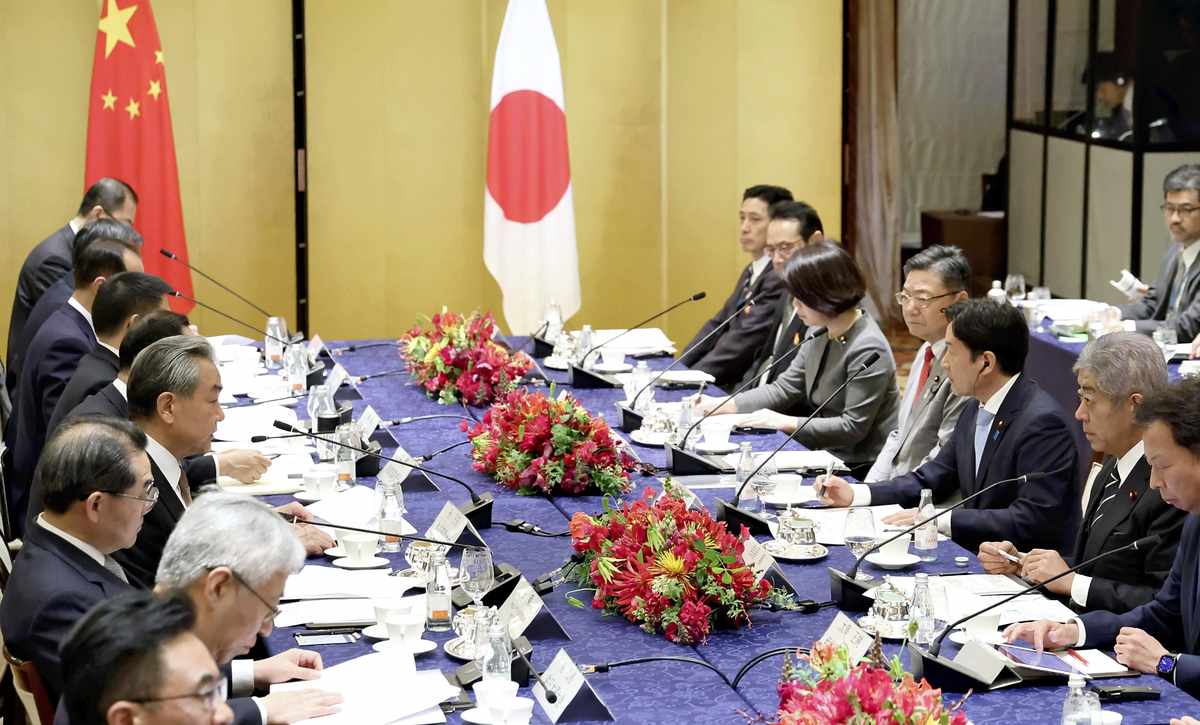

The Japanese and Chinese governments hold a high-level economic dialogue in Tokyo in March, the first such meeting in six years.
8:00 JST, July 12, 2025
As Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba’s ruling Liberal Democratic Party is reported to be in a difficult situation heading into the House of Councillors election on July 20, moves to support the Ishiba administration are noticeable from the administration of Chinese President Xi Jinping.
On June 29, just before the July 3 announcement of the upper house election, the Chinese government announced that it would resume imports of Japanese seafood products to China. Seafood products from 10 prefectures, including Fukushima, will remain subject to the embargo, but seafood products from the other 37 prefectures will now be able to be imported. Imports are expected to resume around August or sooner. The Japanese and Chinese governments agreed on procedures for resuming imports in late May, and this can be said to be the result of smooth progress in their talks, but the timing of the announcement just before the election also reveals China’s political intentions. A source familiar with the inner workings of the Chinese government said, “This is indirect support for the Ishiba administration.” China sent Vice Premier He Lifeng, a close aide to Xi, to China’s National Day at the Osaka Kansai Expo on July 11. He discussed the progress of Japan-China cooperation with LDP Secretary General Hiroshi Moriyama and other Japanese officials.
China has viewed the Ishiba administration, which was inaugurated in October last year, as a very easy partner to work with. Sanae Takaichi, the former minister for economic security who competed with Ishiba for the post of LDP president last year, has a strong conservative tone, visiting Yasukuni Shrine every year, and China judged that there would be no room for progress in Japan-China relations if Takaichi were to lead a new administration. In particular, China was impressed with Ishiba’s views on history, such as his intention to review the Pacific War in light of the upcoming 80th anniversary of the end of the war. According to a Japanese government official, the Chinese side had repeatedly urged the Japanese side at the ambassadorial level to “issue a statement on the 80th anniversary of the end of the war.” There may have been some expectation that the 80th anniversary statement would be more palatable for China than the 70th anniversary statement issued by the conservative administration of Prime Minister Shinzo Abe.
The Chinese side has not been consistently impressed with the Ishiba administration. When Ishiba visited the United States in February this year and met with President Donald Trump shortly after he took office, Ishiba warned China in a bolder manner than usual, joining Trump in saying that he was “opposed to any attempt to unilaterally change the status quo by force or coercion” regarding the situation in Taiwan. China strongly opposed Japan’s decision to draft a joint statement by the Japanese and U.S. leaders in a way that was unfavorable to China on the Taiwan issue, the topic on which China is the most sensitive. Another Japanese government official said at the time, “Japan-China relations suddenly cooled, perhaps because China was displeased by the idea that Japan could cause unpredictable Trump to do something unexpected on the Taiwan issue.”
However, when the Trump administration imposed radical tariff measures in April, Japan-China relations changed again. China was confronted with heavy trade pressure from the United States again, and in a situation where its domestic economy could be seriously affected, China decided that it was important to draw Japan closer. The aforementioned Japanese government official explained: “Japan-China relations made a V-shaped recovery all at once. China has been cozying up to Japan more than it ever has in the last 10 years.”
In May, the United States and China agreed to significantly reduce mutual additional tariffs for 90 days, and in June they agreed to establish a “framework” to implement the May agreement. It can be said that China has achieved a certain degree of detente with the United States (at least regarding tariff measures), but it is unlikely that the Trump administration will change its confrontational stance toward China in the future, and China will likely continue to seek better relations with Japan. As the tariff negotiations between Japan and the United States are proving difficult and there is a rift in Japan-U.S. relations, China may be considering approaching Japan to weaken the Japan-U.S. alliance. In this context, there is no doubt that China believes that the Ishiba administration is convenient for drawing Japan closer. In March, Foreign Minister Wang Yi visited Japan and held the first Japan-China high-level economic dialogue in six years, promising to promote discussions to resume imports of Japanese seafood products. In May, an agreement was reached on procedures for resuming exports. The issue of the restrictions on seafood imports was originally caused by China’s one-sided criticism of the release of treated water from the Fukushima No. 1 nuclear power plant without any scientific evidence, which resulted in China being isolated in the international community and dealing a blow to its own seafood industry. It was the Chinese side that wanted to bring the issue to a close as soon as possible. Since March, China has been indicating a path to gradually resolve this issue, aiming to make it appear as if the issues between Japan and China are making steady progress with the Ishiba administration, which is struggling to run the government as a minority ruling coalition.
However, no matter how many “diplomatic achievements” they produce, it will be difficult to translate them into votes in the House of Councillors election. Japan’s biggest diplomatic challenge at the moment is the U.S. tariff measures, which both the ruling and opposition parties consider a “national crisis,” and relations with China have already been buried as an election issue. A slight improvement in relations with China alone will not improve the domestic evaluation of the Ishiba administration. Unless there is a breakthrough such as a visit by Xi to Japan and major progress on issues between Japan and China, such as the issue of Japanese nationals being detained, the effect will be minimal.
Meanwhile, the Chinese military has intensified its activities near Japan and Taiwan, and there is no sign of it easing up on its security threats. In June, a fighter jet from a Chinese aircraft carrier operating in the Pacific Ocean made an abnormal and dangerous approach to a Maritime Self-Defense Force patrol plane, and in May, a helicopter from the China Coast Guard (a paramilitary organization) violated Japanese territorial airspace around the Senkaku Islands. Behind the facade of its smiling diplomacy, China is steadily making attempts to change the status quo. Does China not realize that many Japanese people have seen through China’s true nature?
Political Pulse appears every Saturday.

Seima Oki
Seima Oki is a deputy editor in the Political News Department of The Yomiuri Shimbun.
Top Articles in Editorial & Columns
-

Riku-Ryu Pair Wins Gold Medal: Their Strong Bond Leads to Major Comeback Victory
-

40 Million Foreign Visitors to Japan: Urgent Measures Should Be Implemented to Tackle Overtourism
-

China Provoked Takaichi into Risky Move of Dissolving House of Representatives, But It’s a Gamble She Just Might Win
-

University of Tokyo Professor Arrested: Serious Lack of Ethical Sense, Failure of Institutional Governance
-

Policy Measures on Foreign Nationals: How Should Stricter Regulations and Coexistence Be Balanced?
JN ACCESS RANKING
-

Japan PM Takaichi’s Cabinet Resigns en Masse
-

Japan Institute to Use Domestic Commercial Optical Lattice Clock to Set Japan Standard Time
-

Israeli Ambassador to Japan Speaks about Japan’s Role in the Reconstruction of Gaza
-

Man Infected with Measles Reportedly Dined at Restaurant in Tokyo Station
-

Videos Plagiarized, Reposted with False Subtitles Claiming ‘Ryukyu Belongs to China’; Anti-China False Information Also Posted in Japan